interpreting tympanogram|Tympanometry : Bacolod Tympanogram tracings are classified as type A (normal), type B (flat, clearly abnormal), and type C (indicating a significantly negative pressure in the middle ear, possibly indicative of. Shining Star Jackpot – If our second-biggest new jackpot hasn’t been won by the time it reaches max . This Promotion is open to Online & Mobile verified Coral account holders aged 18 years or over betting in either £/€ currency whose betting accounts are registered in the UK & Republic of Ireland that are eligible to receive Casino .
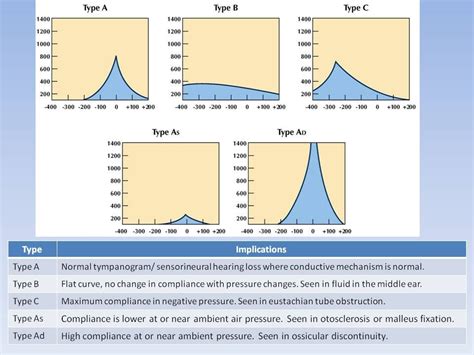
interpreting tympanogram,Tympanogram: Interpreting impedance results. Tympanometry is a test of middle ear functioning. It looks at the flexibility (compliance) of the eardrum to changing air pressures, indicating how effectively sound is transmitted . Tympanogram tracings are classified as type A (normal), type B (flat, clearly abnormal), and type C (indicating a significantly negative pressure in the middle ear, possibly indicative of.interpreting tympanogram Tympanometry Types and Interpretation: 1. A: normal peak between –100 and +100 daPa. 2. A’s’: “shallow” peak (reduced compliance), TM stiff; suggests otosclerosis or tympanosclerosis. 3. A’d’: “deep” peak .

Tympanometry is a method of testing the function of the middle ear. Unlike audiometry, it does not test the ear’s sensitivity to sound or the hearing threshold of the patient. Instead, it is used to detect if sound, when .
Understanding a tympanogram needs expertise, so it's best interpreted by audiologists, ear, nose, and throat specialists, otolaryngologists, or other qualified healthcare professionals. They can use the tympanogram . How to Interpret 1000 Hz Tympanograms. Introductory. 10 mins. Reading. 21 December 2021. Description. The information provided in this answer is derived from .
This guide provides a structured approach to interpreting an audiogram (hearing test) in an OSCE setting. You may also be interested in our guides to performing an ear examination and interpreting Rinne’s .Tympanometry also called tympanometry impedance testing, is a clinical test measuring tympanic membrane mobility to detect problems in the middle ear and is graphically displayed as a tympanogram.Tympanometry is used in conjunction with otoscopy to identify deviations from normal, such as the presence of middle ear fluid, tympanic membrane (TM) perforation and . More than 16% of adult Americans experience some degree of hearing loss.[1] Accurately diagnosing and managing hearing loss is essential in patients of all ages, whether for safety and quality of life in . a tympanogram. A tympanogram is a graphic representation of how the eardrum moves in response to the air pressure in the ear canal. When the eardrum is activated by a sound wave, part of .An audiogram is a hearing test conducted under ideal listening conditions in a soundproof booth. The test includes different pitches and intensities and the results are conveyed in graphical form. If there is hearing loss an audiogram helps distinguish conductive loss (outer/middle ear) from sensorineural loss (cochlea/cochlear nerve).Tympanometry Tympanogram tracings are classified as type A (normal), type B (flat, clearly abnormal), and type C (indicating a significantly negative pressure in the middle ear, . Interpreting Results . A machine records the movement on a tympanogram, a device that depicts the results in graph form. The device will show if your eardrum moves correctly if it's too stiff, too wobbly, or if there is a hole in it. Essentially, the test is used to detect if you have an ear infection, blockages in the canal, or a hole in your eardrum. .
Introduction. Tympanometry is the measurement of the acoustic immittance of the ear as a function of the ear canal pressure. It was introduced by Terkildsen and Thomsen [] as a method of evaluating the middle ear pressure, and has become a routine component of the audiologic and otologic evaluation process worldwide.Tympanometry . GENERAL Audiograms are used to diagnose and monitor hearing loss. Audiograms are created by plotting the thresholds at which a patient can hear various frequencies. Hearing loss can be divided into two categories: conductive or sensorineural. The results of an audiogram can help direct medical and surgical interventions to .Interpreting a Type B (flat) tympanogram volume •Type B w/ abnormally large volume(>1.0 cm3in children, >2.0 cm3in adults) indicates perforated TM or patent (open) PE tube •Type B w/ abnormally small volume (at or close to 0 cm3) indicates impacted cerumen or clogged probe tip •Type B w/ normal volume indicates fluid in the middle ear. The prevalence of hearing loss varies with age, affecting at least 25 percent of patients older than 50 years and more than 50 percent of those older than 80 years. Adolescents and young adults .
The numbers in the description of each curve represents the number of peaks in the curve, e.g. 1B1G stands for 1 peak in the conductance curve and 1 peak in the susceptance, where as 3B1G would indicate 3 peaks in the susceptance curve. To be considered a normal notched tympanogram, Van Camp et al. (1986) 4 created the .interpreting tympanogram The shape of the tympanogram will show whether your results are normal or abnormal. Normal results mean your eardrum is moving as it should. If your eardrum moves normally, the line on the graph will appear curved, like a hill or mountain. The highest part of the curve, or the mountain “peak,” will happen between -100 and +100 daPa on the .

In this webinar, you will learn:1) How to measure a tympanogram2) How to interpret tympanograms using quantitative analysis and Jerger's classification3) How.The first step in interpreting tympanometric data is to gain a thorough understanding of the basic principles underlying all acoustic-immittance measurements. . Tympanogram format. If an external recording .tympanogram). Seeing a type A or A s tympanogram in the setting of ipsilateral conductive hearing loss should raise suspicion that otosclerosis is the underlying disease causing the ab- normal audiometric findings.22 More information on tympanometry will be discussed in Section 3. The following audiogram grids are representative of these patterns.
A tympanogram is a graphic display of tympanometric data. Tympanometry is appealing in an otolaryngology practice because it provides a rapid, atraumatic, and objective technique for 1. . This example points out the importance of an otoscopic examination in interpreting tympanometric data. Multiple Frequency Tympanometry .The audiogram below gives you an idea of the different levels of hearing loss and where on the graph they would appear. It is probably a reverse of what you mightInterpreting a Pure-tone Audiogram (PTA) An audiogram is a plot of frequency in Hertz (Hz) against intensity measured in decibels hearing level (dB HL). The frequency range for a PTA is 250 Hz to 8000Hz as this range of frequencies is similar to the range important for speech understanding. . Interpreting a Tympanogram. Tympanogram is graphic . In the presence of a Type C tympanogram, depending on the degree of negative pressure in the middle ear, reflexes can be either present or absent. If acoustic reflexes are present in the probe ear, it is unlikely that a conductive hearing loss exists, except in the rare case of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence (SSCD). .
interpreting tympanogram|Tympanometry
PH0 · Understanding and Interpreting a Tympanogram
PH1 · Tympanometry: An Introduction
PH2 · Tympanometry test
PH3 · Tympanometry
PH4 · Interpreting the tests – Audiogram and Tympanogram
PH5 · Interpreting the tests – Audiogram and Tympanogram
PH6 · How to interpret a tympanogram
PH7 · How to Read and Interpret Normal and Abnormal Tympanogram Result
PH8 · How to Read and Interpret Normal and Abnormal Tympanogram
PH9 · How to Interpret 1000 Hz Tympanograms
PH10 · Audiogram Interpretation